There are no chance of me to write Anagram check in C#.
Let's see some article posted.
It says he met anagram question with code interview and answer was as follows.
def anagram(s1, s2) s1.chars.sort == s2.chars.sort end
Let's try in C#.
Contents
- Contents
- Enumerable.Except
- O(n log n) : Sort with Enumerable.SequenceEqual
- O(n) : Dictionary
- Conclusion
Enumerable.Except
First, I thought it's not good to use Sort for performance issue, and imagine to use Enumerable.Except.
But soon I forgive it. Except will be worth when duplicate character is accepted but may take too much check if no allowed. You can see #7 failed with "aba == bab" was true!

Same issue will happen with Enumerable.All.
https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb548541(v=vs.100).aspx

O(n log n) : Sort with Enumerable.SequenceEqual
May be one of the easiest way is sort array then check. Let's use Enumerable.SequenceEqual() to sorted array.
Enumerable.SequenceEqual Method (System.Linq) | Microsoft Learn
It passes all tests. But is O(n log n)....
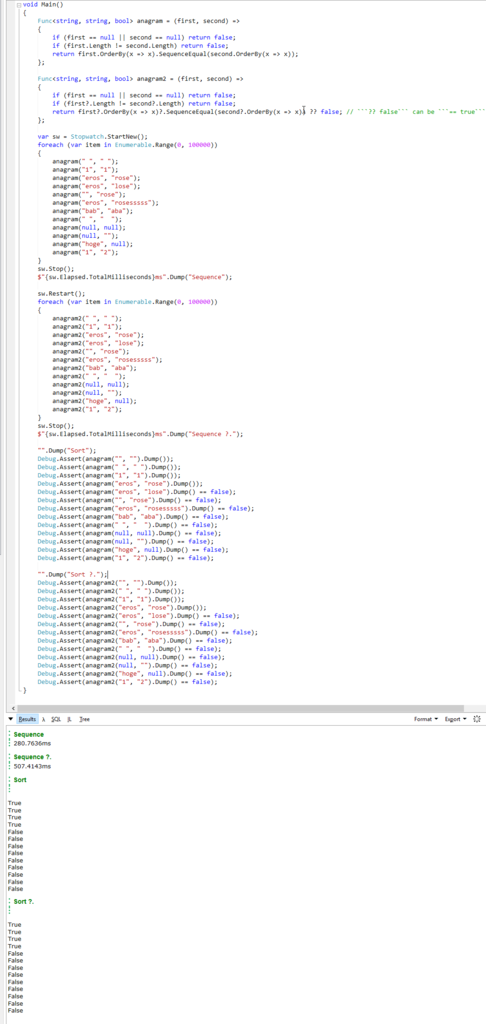
string null conditional check ?. will cause duplicate null check, so it may take bit more time.
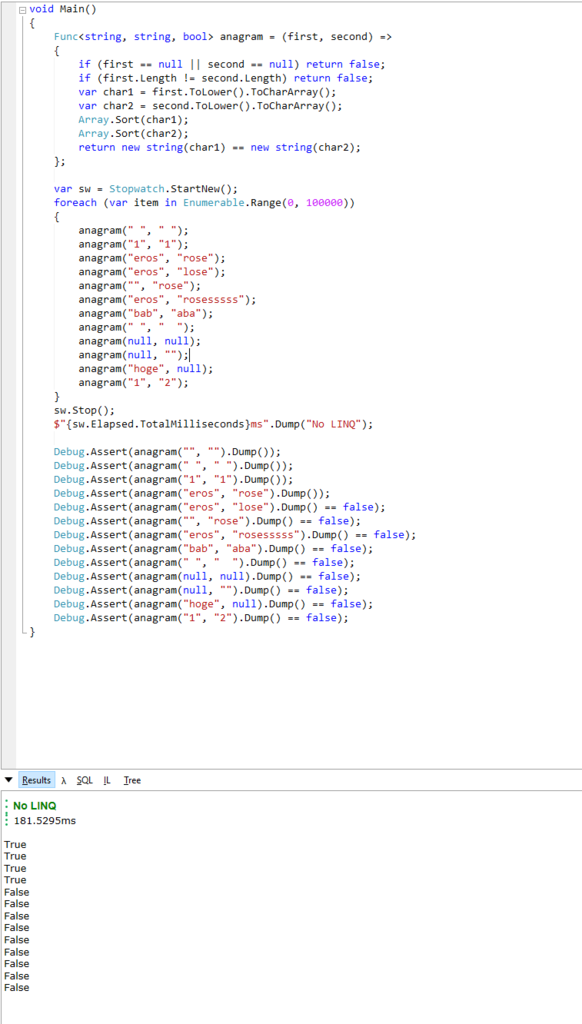
No LINQ
I like LINQ but let's try no LINQ. Looks like better performance, 181ms.
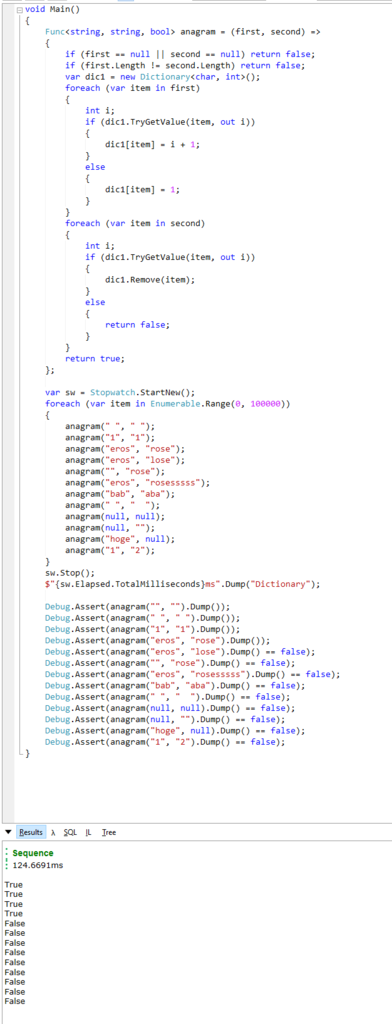
O(n) : Dictionary
Let's remove sort and just count with Dictionary. This bring much better performance, only 124ms.
Also here's my friend @ichiohta's code.
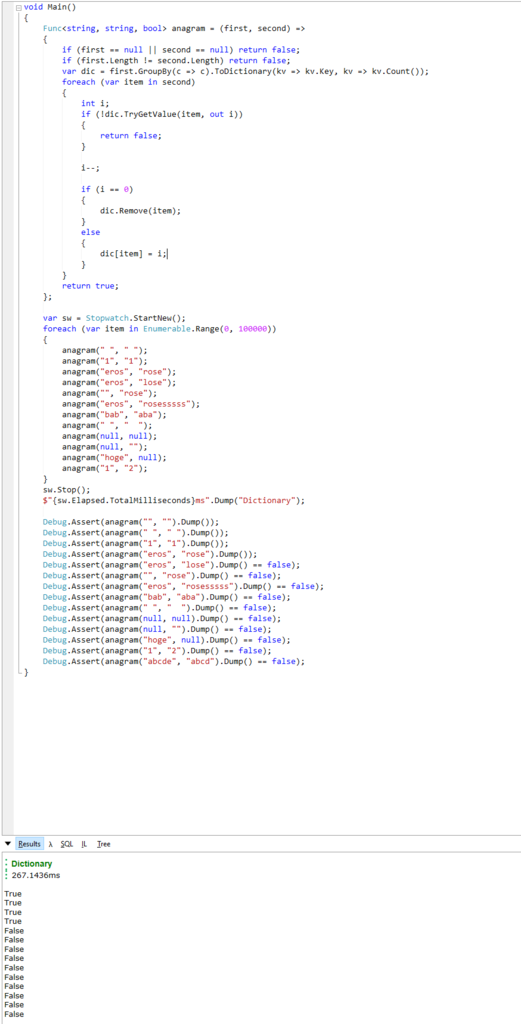
It takes much time in .GroupBy().ToDictionary(). Swap with my code brings 267ms -> 127ms.

Dictionary is much better performance than Sort algorithm.
Conclusion
| Pattern | Algorithm | time in 12 test x 100000 |
|---|---|---|
| Sort (LINQ : Enumerable.SequenceEqual) | O(n log n) |
280ms |
| Sort (LINQ : Enumerable.SequenceEqual + ?.) | O(n log n) |
290ms - 580ms |
| Sort (NO LINQ) | O(n log n) |
181ms |
| Dictionary (NO LINQ) | O(n) |
124ms |
| Dictionary (LINQ : GroupBy().ToDictionary()) | O(n) |
267ms |
What's the most readable and fast enough code for you? More idea is much appreciated.